Build Your First Voice Assistant
Hone your practical speech recognition application skills with this overview of building a voice assistant using Python.
Nowadays, it isn’t surprising to hear someone speak to someone that isn’t there. We ask Alexa for the weather and to turn the temperature down on the thermostat. Then, we ask Siri what our schedule for the day is and to call people. We are connected now more than ever using our voice and voice interface technology. I can’t imagine doing things manually anymore! It’s truly the future.
— Forbes
Introduction
Who doesn't want to have the luxury to own an assistant who always listens for your call, anticipates your every need, and takes action when necessary? That luxury is now available thanks to artificial intelligence-based voice assistants.
Voice assistants come in somewhat small packages and can perform a variety of actions after hearing your command. They can turn on lights, answer questions, play music, place online orders and do all kinds of AI-based stuff.
Voice assistants are not to be confused with virtual assistants, which are people who work remotely and can, therefore, handle all kinds of tasks. Rather, voice assistants are technology based. As voice assistants become more robust, their utility in both the personal and business realms will grow as well.
What is a Voice Assistant?
A voice assistant or intelligent personal assistant is a software agent that can perform tasks or services for an individual based on verbal commands i.e. by interpreting human speech and respond via synthesized voices. Users can ask their assistants’ questions, control home automation devices, and media playback via voice, and manage other basic tasks such as email, to-do lists, open or close any application etc with verbal commands.
Let me give you the example of Braina (Brain Artificial) which is an intelligent personal assistant, human language interface, automation and voice recognition software for Windows PC. Braina is a multi-functional AI software that allows you to interact with your computer using voice commands in most of the languages of the world. Braina also allows you to accurately convert speech to text in over 100 different languages of the world.
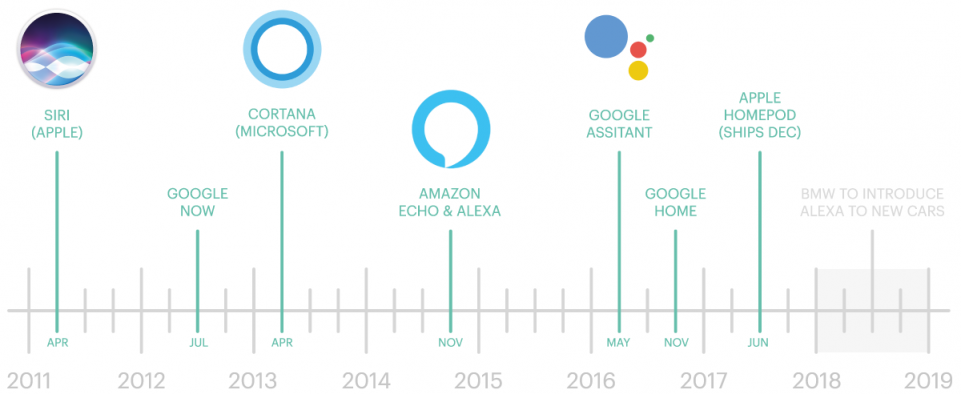
History of Voice Assistants
In recent times, Voice assistants got the major platform after Apple integrated the most astonishing Virtual Assistant — Siri which is officially a part of Apple Inc. But the timeline of greatest evolution began with the year 1962 event at the Seattle World Fair where IBM displayed a unique apparatus called Shoebox. It was the actual size of a shoebox and could perform scientific functions and can perceive 16 words and also speak them in the human recognizable voice with 0 to 9 numerical digits.
During the period of the 1970s, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania — with the considerable help of the U.S Department of Defence and its Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) — made Harpy. It could understand almost 1,000 words, which is approximately the vocabulary of a three-year-old child.
Big organizations like Apple and IBM sooner in the 90s started to make things that utilized voice acknowledgment. In 1993, Macintosh began to building speech recognition with its Macintosh PCs with PlainTalk.
In April 1997, Dragon NaturallySpeaking was the first constant dictation product which could comprehend around 100 words and transform it into readable content.
Having said that, how cool it would be to build a simple voice-based desktop/laptop assistant that has the capability to:
- Open the subreddit in the browser.
- Open any website in the browser.
- Send an email to your contacts.
- Launch any system application.
- Tells you the current weather and temperature of almost any city
- Tells you the current time.
- Greetings
- Play you a song on VLC media player(of course you need to have VLC media player installed in your laptop/desktop)
- Change desktop wallpaper.
- Tells you latest news feeds.
- Tells you about almost anything you ask.
So here in this article, we are going to build a voice-based application which is capable of doing all the above-mentioned tasks. But first, check out this video below which I made while I was interacting with the desktop voice assistant and I call her Sofia.
New video by Nagesh Chauhan
Interaction with Sofia
I hope you guys have liked the above video in which I was interacting with Sofia. Now let’s start building this cool thing…
Dependencies and requirements :
System requirements: Python 2.7, Spyder IDE, MacOS Mojave(version 10.14)
Install all these python libraries :
pip install SpeechRecognition pip install beautifulsoup4 pip install vlc pip install youtube-dl pip install pyowm pip install wikipedia
Let’s start building our desktop voice assistant using python
Start by importing all the required libraries :
import speech_recognition as sr
import os
import sys
import re
import webbrowser
import smtplib
import requests
import subprocess
from pyowm import OWM
import youtube_dl
import vlc
import urllib
import urllib2
import json
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as soup
from urllib2 import urlopen
import wikipedia
import random
from time import strftime
For our voice-assistant to perform all the above-discussed features, we have to code the logic of each of them in one method.
So our first step is to create the method which will interpret user voice response.
def myCommand():
r = sr.Recognizer()
with sr.Microphone() as source:
print('Say something...')
r.pause_threshold = 1
r.adjust_for_ambient_noise(source, duration=1)
audio = r.listen(source)
try:
command = r.recognize_google(audio).lower()
print('You said: ' + command + '\n')
#loop back to continue to listen for commands if unrecognizable speech is received
except sr.UnknownValueError:
print('....')
command = myCommand();
return command
Next, create a method that will convert text to speech.
def sofiaResponse(audio):
print(audio)
for line in audio.splitlines():
os.system("say " + audio)
Now create a loop to continue executing multiple commands. Inside the method assistant() passing user command(myCommand()) as parameters.
while True:
assistant(myCommand())
Our next step is to create multiple if statements corresponding to each of the features. So let us see how to create these small modules inside if statement for each command.
1. Open the subreddit Reddit in the browser.
The user will give any command to open any subreddit from Reddit and the command should be “Hey Sofia! Can you please open Reddit subreddit_name”. only the italic bold phrase should be used as it is. You can use any kind of prefix, just take care of the italic bold phrase.
How it works : If you have said the phrase open reddit in your command then it will search for subreddit name in the user command using re.search(). The subreddit will be searched using www.reddit.com and will get opened in the browser using pythons Webbrowser module.The Webbrowser module provides a high-level interface to allow displaying Web-based documents to users.
if 'open reddit' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('open reddit (.*)', command)
url = 'https://www.reddit.com/'
if reg_ex:
subreddit = reg_ex.group(1)
url = url + 'r/' + subreddit
webbrowser.open(url)
sofiaResponse('The Reddit content has been opened for you Sir.')
So, the above code will open your desired Reddit in your default browser.
2. Open any website in the browser.
You can open any website just be saying “open website.com” or “open website.org”.
For example: “Please open facebook.com” or “Hey, can you open linkedin.com” like this you can ask Sofia to open any website for you.
How it works : If you have said the word open in your command then it will search for website name in the user command using re.search(). Next, it will append the website name to https://www. and using webbrowser module the complete URL gets opened in the browser.
elif 'open' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('open (.+)', command)
if reg_ex:
domain = reg_ex.group(1)
print(domain)
url = 'https://www.' + domain
webbrowser.open(url)
sofiaResponse('The website you have requested has been opened for you Sir.')
else:
pass
3. Send Email.
You can also ask your desktop assistant to send the email.
How it works : If you have said the word email in your command then the bot will ask for receipient, If my response is rajat, the bot will use pthons smtplib library. The smtplib module defines an SMTP client session object that can be used to send mail to any Internet machine with an SMTP or ESMTP listener daemon. Sending mail is done with Python’s smtplib using an SMTP server. First it will initaite gmail SMTP using smtplib.SMTP(), then identify the server using ehlo() function, then encypting the session starttls(), then login to your mailbox using login(), then sending the message using sendmail().
elif 'email' in command:
sofiaResponse('Who is the recipient?')
recipient = myCommand()if 'rajat' in recipient:
sofiaResponse('What should I say to him?')
content = myCommand()
mail = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.gmail.com', 587)
mail.ehlo()
mail.starttls()
mail.login('your_email_address', 'your_password')
mail.sendmail('sender_email', 'receiver_email', content)
mail.close()
sofiaResponse('Email has been sent successfuly. You can check your inbox.')else:
sofiaResponse('I don\'t know what you mean!')
4. Launch any system application.
Say “launch calendar” or “can you please launch skype” or “Sofia launch finder” etc. and Sofia will launch that system application for you.
How it works : If you have said the word launch in your command then it will search for application name(if it is present in your system) in the user command using re.search(). It will then append the suffix “.app” to the application name. Now your application name is for example say calender.app(In macOS the executable files end with extension .app unlike in Windows which ends with .exe). So the executable application name will be launched using python subprocess’s Popen() function. The subprocess module enables you to start new applications from your Python program.
elif 'launch' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('launch (.*)', command)
if reg_ex:
appname = reg_ex.group(1)
appname1 = appname+".app"
subprocess.Popen(["open", "-n", "/Applications/" + appname1], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)sofiaResponse('I have launched the desired application')
5. Tells you the current weather and temperature of almost any city.
Sofia can also tell you the weather, maximum and minimum temperature of any city around the world. The user just needs to say something like “what is the current weather in London” or “tell me the current weather in Delhi”.
How it works : If you have said the phrase current weather in your command then it will search for city name using re.search(). I have used pythons pyowm library to get the weather of any city. get_status() will tell you about the weather condition like haze, cloudy, rainy etc and get_temperature() will tell you about the max and min temperature of the city.
elif 'current weather' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('current weather in (.*)', command)
if reg_ex:
city = reg_ex.group(1)
owm = OWM(API_key='ab0d5e80e8dafb2cb81fa9e82431c1fa')
obs = owm.weather_at_place(city)
w = obs.get_weather()
k = w.get_status()
x = w.get_temperature(unit='celsius')
sofiaResponse('Current weather in %s is %s. The maximum temperature is %0.2f and the minimum temperature is %0.2f degree celcius' % (city, k, x['temp_max'], x['temp_min']))
6. Tells you the current time.
“Sofia can you tell me the current time ?” or “what is the time now ?” and Sofia will tell you the current time of your timezone.
How it works : Its pretty simple
elif 'time' in command:
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
sofiaResponse('Current time is %d hours %d minutes' % (now.hour, now.minute))
7. Greetings/ leave
Say “hello Sofia” to greet your voice assistant or when you want the program to terminate say something like “shutdown Sofia” or “Sofia please shutdown” etc.
How it works : If you have said the word hello in your command, then depending on the time of the day, the bot will greet the user. If the time is more than 12 noon, the bot will respond “Hello Sir. Good afternoon”, likewise if the time is more than 6 ck pm, the bot will respond “Hello Sir. Good evening”. And when you give command as shutdown, sys.exit() will be called to terminate the program.
#Greet Sofia
elif 'hello' in command:
day_time = int(strftime('%H'))
if day_time < 12:
sofiaResponse('Hello Sir. Good morning')
elif 12 <= day_time < 18:
sofiaResponse('Hello Sir. Good afternoon')
else:
sofiaResponse('Hello Sir. Good evening')#to terminate the program
elif 'shutdown' in command:
sofiaResponse('Bye bye Sir. Have a nice day')
sys.exit()
8. Play you a song on VLC media player
This feature allows your voice bot to play your desired song in VLC media player. The user will say “Sofia play me a song”, the bot will ask “What song shall I play Sir?”. Just say the name of the song and Sofia will download the song from youtube in your local drive, play that song on the VLC media player and if you again play a song the previously downloaded song will get deleted automatically.
How it works :If you have said the phrase play me a song in your command, then it will ask you what video song to play. The song you will ask will be searched in youtube.com, If found than the song will be downloaded in your local directory using pythons youtube_dl library. The youtube-dl is a command-line program to download videos from YouTube.com and a few more sites. Now the song will be played as soon as it gets downloded using pythons VLC library and play(path_to__videosong) module actually playes the song.
Now if the next time you ask for any other song, the local directory will be flushed and a new song will be downloaded in that directory.
elif 'play me a song' in command:
path = '/Users/nageshsinghchauhan/Documents/videos/'
folder = path
for the_file in os.listdir(folder):
file_path = os.path.join(folder, the_file)
try:
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
os.unlink(file_path)
except Exception as e:
print(e)sofiaResponse('What song shall I play Sir?')mysong = myCommand()
if mysong:
flag = 0
url = "https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=" + mysong.replace(' ', '+')
response = urllib2.urlopen(url)
html = response.read()
soup1 = soup(html,"lxml")
url_list = []
for vid in soup1.findAll(attrs={'class':'yt-uix-tile-link'}):
if ('https://www.youtube.com' + vid['href']).startswith("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v="):
flag = 1
final_url = 'https://www.youtube.com' + vid['href']
url_list.append(final_url)url = url_list[0]
ydl_opts = {}os.chdir(path)
with youtube_dl.YoutubeDL(ydl_opts) as ydl:
ydl.download([url])
vlc.play(path)if flag == 0:
sofiaResponse('I have not found anything in Youtube ')
9. Change desktop wallpaper.
You guys can also change your desktop wallpaper using this feature. When you say something like “change wallpaper” or “Sofia please change wallpaper” the bot will download random wallpaper from unsplash.comand sets it as your desktop background.
How it works : If you have said the phrase change wallpaper in your command, the program will download a random wallpaper from unsplash.com, store it in local directory and set it as your desktop wallpaper using subprocess.call(). I have used unsplash API to get access to its content.
Now if the next time you ask to change the wallpaper again, your local directory will be flushed and a new wallpaper will be downloaded in that directory.
elif 'change wallpaper' in command:
folder = '/Users/nageshsinghchauhan/Documents/wallpaper/'
for the_file in os.listdir(folder):
file_path = os.path.join(folder, the_file)
try:
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
os.unlink(file_path)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
api_key = 'fd66364c0ad9e0f8aabe54ec3cfbed0a947f3f4014ce3b841bf2ff6e20948795'
url = 'https://api.unsplash.com/photos/random?client_id=' + api_key #pic from unspalsh.com
f = urllib2.urlopen(url)
json_string = f.read()
f.close()
parsed_json = json.loads(json_string)
photo = parsed_json['urls']['full']
urllib.urlretrieve(photo, "/Users/nageshsinghchauhan/Documents/wallpaper/a") # Location where we download the image to.
subprocess.call(["killall Dock"], shell=True)
sofiaResponse('wallpaper changed successfully')
10. Tells you latest news feeds.
Sofia can also tell you the latest news update. The user just has to say “Sofia what are the top news for today ?” or “tell me the news for today”.
How it works : If you have said the phrase news for today in your command then it will scrape data using Beautiful Soup from Google News RSS() and read it for you. For convineince I have set number of news limit to 15.
elif 'news for today' in command:
try:
news_url="https://news.google.com/news/rss"
Client=urlopen(news_url)
xml_page=Client.read()
Client.close()
soup_page=soup(xml_page,"xml")
news_list=soup_page.findAll("item")
for news in news_list[:15]:
sofiaResponse(news.title.text.encode('utf-8'))
except Exception as e:
print(e)
11. Tells you about almost anything you ask.
Your bot can fetch details of almost anything you ask her. Like “Sofia tell me about Google” or “Please tell me about Supercomputers” or “please tell me about the Internet”. So as you can see you can ask about almost anything.
How it works : If you have said the phrase tell me about in your command then it will search for the keyword in the user command using re.search(). Using pythons wikipedia library it will search for that topic and extract first 500 characters(if you dont specify the limit the bot will read the whole page for you). Wikipedia is a Python library that makes it easy to access and parse data from Wikipedia.
elif 'tell me about' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('tell me about (.*)', command)
try:
if reg_ex:
topic = reg_ex.group(1)
ny = wikipedia.page(topic)
sofiaResponse(ny.content[:500].encode('utf-8'))
except Exception as e:
sofiaResponse(e)
Let's put everything together
import speech_recognition as sr
import os
import sys
import re
import webbrowser
import smtplib
import requests
import subprocess
from pyowm import OWM
import youtube_dl
import vlc
import urllib
import urllib2
import json
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as soup
from urllib2 import urlopen
import wikipedia
import random
from time import strftimedef sofiaResponse(audio):
"speaks audio passed as argument"
print(audio)
for line in audio.splitlines():
os.system("say " + audio)def myCommand():
"listens for commands"
r = sr.Recognizer()
with sr.Microphone() as source:
print('Say something...')
r.pause_threshold = 1
r.adjust_for_ambient_noise(source, duration=1)
audio = r.listen(source)
try:
command = r.recognize_google(audio).lower()
print('You said: ' + command + '\n')
#loop back to continue to listen for commands if unrecognizable speech is received
except sr.UnknownValueError:
print('....')
command = myCommand();
return commanddef assistant(command):
"if statements for executing commands"#open subreddit Reddit
if 'open reddit' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('open reddit (.*)', command)
url = 'https://www.reddit.com/'
if reg_ex:
subreddit = reg_ex.group(1)
url = url + 'r/' + subreddit
webbrowser.open(url)
sofiaResponse('The Reddit content has been opened for you Sir.')elif 'shutdown' in command:
sofiaResponse('Bye bye Sir. Have a nice day')
sys.exit()#open website
elif 'open' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('open (.+)', command)
if reg_ex:
domain = reg_ex.group(1)
print(domain)
url = 'https://www.' + domain
webbrowser.open(url)
sofiaResponse('The website you have requested has been opened for you Sir.')
else:
pass#greetings
elif 'hello' in command:
day_time = int(strftime('%H'))
if day_time < 12:
sofiaResponse('Hello Sir. Good morning')
elif 12 <= day_time < 18:
sofiaResponse('Hello Sir. Good afternoon')
else:
sofiaResponse('Hello Sir. Good evening')elif 'help me' in command:
sofiaResponse("""
You can use these commands and I'll help you out:1. Open reddit subreddit : Opens the subreddit in default browser.
2. Open xyz.com : replace xyz with any website name
3. Send email/email : Follow up questions such as recipient name, content will be asked in order.
4. Current weather in {cityname} : Tells you the current condition and temperture
5. Hello
6. play me a video : Plays song in your VLC media player
7. change wallpaper : Change desktop wallpaper
8. news for today : reads top news of today
9. time : Current system time
10. top stories from google news (RSS feeds)
11. tell me about xyz : tells you about xyz
""")#joke
elif 'joke' in command:
res = requests.get(
'https://icanhazdadjoke.com/',
headers={"Accept":"application/json"})
if res.status_code == requests.codes.ok:
sofiaResponse(str(res.json()['joke']))
else:
sofiaResponse('oops!I ran out of jokes')#top stories from google news
elif 'news for today' in command:
try:
news_url="https://news.google.com/news/rss"
Client=urlopen(news_url)
xml_page=Client.read()
Client.close()
soup_page=soup(xml_page,"xml")
news_list=soup_page.findAll("item")
for news in news_list[:15]:
sofiaResponse(news.title.text.encode('utf-8'))
except Exception as e:
print(e)#current weather
elif 'current weather' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('current weather in (.*)', command)
if reg_ex:
city = reg_ex.group(1)
owm = OWM(API_key='ab0d5e80e8dafb2cb81fa9e82431c1fa')
obs = owm.weather_at_place(city)
w = obs.get_weather()
k = w.get_status()
x = w.get_temperature(unit='celsius')
sofiaResponse('Current weather in %s is %s. The maximum temperature is %0.2f and the minimum temperature is %0.2f degree celcius' % (city, k, x['temp_max'], x['temp_min']))#time
elif 'time' in command:
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
sofiaResponse('Current time is %d hours %d minutes' % (now.hour, now.minute))elif 'email' in command:
sofiaResponse('Who is the recipient?')
recipient = myCommand()
if 'rajat' in recipient:
sofiaResponse('What should I say to him?')
content = myCommand()
mail = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.gmail.com', 587)
mail.ehlo()
mail.starttls()
mail.login('your_email_address', 'your_password')
mail.sendmail('sender_email', 'receiver_email', content)
mail.close()
sofiaResponse('Email has been sent successfuly. You can check your inbox.')
else:
sofiaResponse('I don\'t know what you mean!')#launch any application
elif 'launch' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('launch (.*)', command)
if reg_ex:
appname = reg_ex.group(1)
appname1 = appname+".app"
subprocess.Popen(["open", "-n", "/Applications/" + appname1], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)sofiaResponse('I have launched the desired application')#play youtube song
elif 'play me a song' in command:
path = '/Users/nageshsinghchauhan/Documents/videos/'
folder = path
for the_file in os.listdir(folder):
file_path = os.path.join(folder, the_file)
try:
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
os.unlink(file_path)
except Exception as e:
print(e)sofiaResponse('What song shall I play Sir?')
mysong = myCommand()
if mysong:
flag = 0
url = "https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=" + mysong.replace(' ', '+')
response = urllib2.urlopen(url)
html = response.read()
soup1 = soup(html,"lxml")
url_list = []
for vid in soup1.findAll(attrs={'class':'yt-uix-tile-link'}):
if ('https://www.youtube.com' + vid['href']).startswith("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v="):
flag = 1
final_url = 'https://www.youtube.com' + vid['href']
url_list.append(final_url)url = url_list[0]
ydl_opts = {}os.chdir(path)
with youtube_dl.YoutubeDL(ydl_opts) as ydl:
ydl.download([url])
vlc.play(path)if flag == 0:
sofiaResponse('I have not found anything in Youtube ')#change wallpaper
elif 'change wallpaper' in command:
folder = '/Users/nageshsinghchauhan/Documents/wallpaper/'
for the_file in os.listdir(folder):
file_path = os.path.join(folder, the_file)
try:
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
os.unlink(file_path)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
api_key = 'fd66364c0ad9e0f8aabe54ec3cfbed0a947f3f4014ce3b841bf2ff6e20948795'
url = 'https://api.unsplash.com/photos/random?client_id=' + api_key #pic from unspalsh.com
f = urllib2.urlopen(url)
json_string = f.read()
f.close()
parsed_json = json.loads(json_string)
photo = parsed_json['urls']['full']
urllib.urlretrieve(photo, "/Users/nageshsinghchauhan/Documents/wallpaper/a") # Location where we download the image to.
subprocess.call(["killall Dock"], shell=True)
sofiaResponse('wallpaper changed successfully')#askme anything
elif 'tell me about' in command:
reg_ex = re.search('tell me about (.*)', command)
try:
if reg_ex:
topic = reg_ex.group(1)
ny = wikipedia.page(topic)
sofiaResponse(ny.content[:500].encode('utf-8'))
except Exception as e:
print(e)
sofiaResponse(e)sofiaResponse('Hi User, I am Sofia and I am your personal voice assistant, Please give a command or say "help me" and I will tell you what all I can do for you.')#loop to continue executing multiple commands
while True:
assistant(myCommand())
So you have seen how just by writing simple lines of python code we can create a very cool voice-based desktop/laptop assistant. Apart from these features, you can also include many different features in your voice assistant.
Please not that once you start executing your program, be loud and clear while you are interacting with voice assistant because it may happen that if your voice is not clear your voice assistant may not be able to interpret you properly.
Conclusion: What the future holds
Throughout the history of computing, user interfaces have become progressively natural to use. The screen and keyboard were one step in this direction. The mouse and graphical user interface were another. Touch screens are the most recent development. The next step will most likely consist of a mix of augmented reality, gestures and voice commands. After all, it is often easier to ask a question or have a conversation than it is to type something or enter multiple details in an online form.
The more a person interacts with voice-activated devices, the more trends, and patterns the system identifies based on the information it receives. Then, this data can be utilized to determine user preferences and tastes, which is a long-term selling point for making a home smarter. Google and Amazon are looking to integrate voice-enabled artificial intelligence capable of analyzing and responding to human emotion.
I hope you guys have enjoyed reading this article. Share your thoughts/comments/doubts in the comment section. You can reach me out over LinkedIn.
Bio: Nagesh Singh Chauhan is a Big data developer at CirrusLabs. He has over 4 years of working experience in various sectors like Telecom, Analytics, Sales, Data Science having specialisation in various Big data components.
Original. Reposted with permission.
Related:
- Practical Speech Recognition with Python: The Basics
- Comparison of the Top Speech Processing APIs
- TensorFlow vs PyTorch vs Keras for NLP