The strategic vision of the manufacturing and automotive treasury function is to deliver efficiency, control, and scalability. The logical structure for this transformation includes several key components: business events, centralized demand deposit accounts with banking connectivity, and a reporting data warehouse.
A comprehensive finance and treasury transformation program can help improve cash and liquidity management, reduce manual processing, automate financial and risk reconciliation, and accelerate financial close. It can also help you enable information delivery and simplify the integration of general ledger and golden source data in reporting.
Finance and treasury transformation ultimately makes your organization more flexible and nimble in order to meet your changing business needs. Below are just some of the problems we frequently see, and how such a program can help you solve them.
CASH BALANCE REPORTING AND LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT
PROBLEM
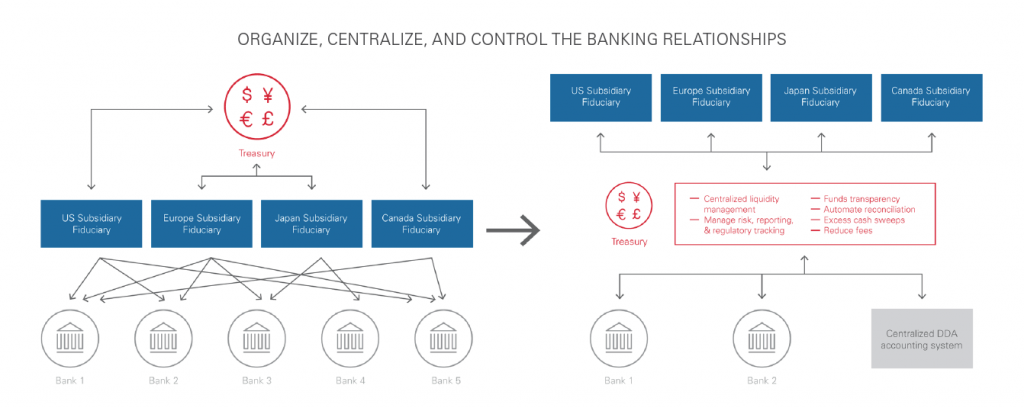
The financial officers in an organization’s subsidiaries have established their own banking relationships, which results in large numbers of accounts and external banks. The use of multiple banking relationships across the globe is expensive and lacks centralized management and oversight. Transaction costs are high and have multi-day settlement periods.
Corporate level cash balance reporting is difficult. Management of liquidity is difficult. The finance officer of the subsidiaries is responsible for “sending” the excess to corporate, which is too late for centralized overnight investment.
Large, multi-billion dollar bond payments require multiple account balance transfers and manual handholding of transactions or fees for a liquidity account, not to mention the associated interest costs.
SOLUTION
Establish an in-house bank with a centralized DDA accounting system with key functions, such as excess cash sweeps and direct payment integration with key banking relationships. This allows subsidiaries to utilize the in-house bank and reduce or eliminate banking relationships. It provides a real-time view of their liquidity to the corporate treasury. This solution should also automatically reconcile transactions and banking balances to in-house balances giving the CFO a daily picture of unreconciled items.
This system can also be a centralized (shadow) DDA accounting system for all bank accounts and provide the automated reconciliation of accounts transactions and balances, or simply provide an automated reconciliation system. This system should be directly integrated with the bank’s statements. This system will also provide the CFO with a centralized list of banking relationships, related costs, and reconciliation function.
Centralizing banking relationships to a universal bank will reduce per-account fees and transaction fees for interbank transfers, allow multi-currency accounts, and centralize FX costs.
ORGANIZATIONAL PROFITABILITY, FORECASTING, AND REPORTING
PROBLEM
Multiple treasury systems are not directly integrated with the general ledger or payment systems. This makes it difficult for the CFO to understand the total picture of liabilities and hedges globally. The risks of derivative transactions are not centrally managed. The costs and hedge effectiveness of derivatives are unclear. This makes it difficult for the CFO to measure return on capital invested in subsidiaries.
SOLUTION
Implement and consolidate into a single treasury management system and create a risk trade warehouse. This system should be directly integrated to the in-house bank for cash management and payments. The system should have built-in hedge effectiveness reporting and also provide a return on capital/return on equity investments reporting.
In addition, a centralized risk warehouse will provide better strategic planning on derivatives reporting and finance industry regulatory changes, such as derivatives clearing and operational efficiencies in trade confirmation and payments. It can also reduce costs and operational risks through netting.
REGULATORY AND COMPLIANCE REPORTING
PROBLEM
Compliance functions such as anti-money laundering, anti-corruption, and other anti-financial crime initiatives are distributed and not measured consistently across subsidiaries exposing the firm to be complicit in fraud.
Operational risk management systems are not consistently updated and maintained, leading to higher capital reserves to cover costs of breaches. The key risk indicator and key process metrics are not consistently managed and reported.
SOLUTION
Implement an operational risk system (ORM) and consistently manage key risk indicators and key processes that mitigate the risks. Tie capital reserves directly to metrics and manage reserves based on metrics.
Integrate the operational risk system to the risk warehouse. The systems that provide ORM require all historical transaction data to be retained and centralized. Both a centralized DDA and a trade warehouse support this function and ensure a more consistent set of data for analytics, and reduce the costs of implementation with fewer data feeds. Missing data and data quality issues can be directly addressed as the sources are centralized and changes can be more easily implemented.
—
If you are interested in learning about Perficient’s finance and treasury transformation services, please complete the contact form at the bottom of this page.