ML internals: Synthetic Minority Oversampling (SMOTE) Technique
Domino Data Lab
MAY 20, 2021
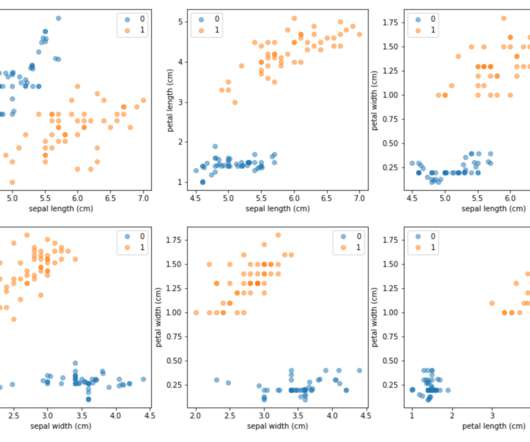
This renders measures like classification accuracy meaningless. In their 2002 paper Chawla et al. 2002) have performed a comprehensive evaluation of the impact of SMOTE- based up-sampling. 2002) provide an example that illustrates the modifications. Generation of artificial examples. Chawla et al., Chawla et al.,












Let's personalize your content