The history of ESG: A journey towards sustainable investing
IBM Big Data Hub
FEBRUARY 8, 2024
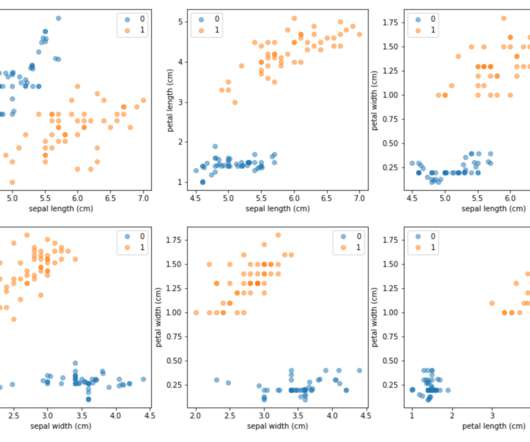
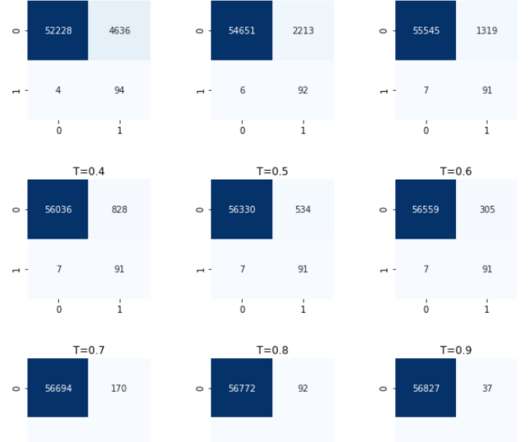
It refers to a set of metrics used to measure an organization’s environmental and social impact and has become increasingly important in investment decision-making over the years. In response, asset managers began to develop ESG strategies and metrics to measure the environmental and social impact of their investments.













Let's personalize your content