5 misconceptions about cloud data warehouses
IBM Big Data Hub
FEBRUARY 2, 2023
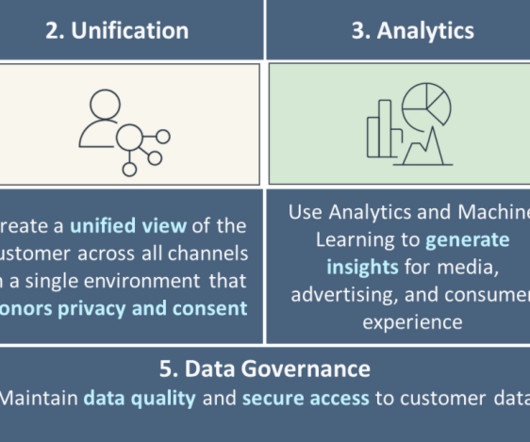
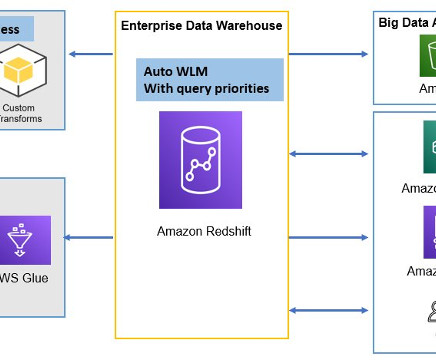
In today’s world, data warehouses are a critical component of any organization’s technology ecosystem. They provide the backbone for a range of use cases such as business intelligence (BI) reporting, dashboarding, and machine-learning (ML)-based predictive analytics, that enable faster decision making and insights.







































Let's personalize your content