Towards optimal experimentation in online systems
The Unofficial Google Data Science Blog
APRIL 23, 2024
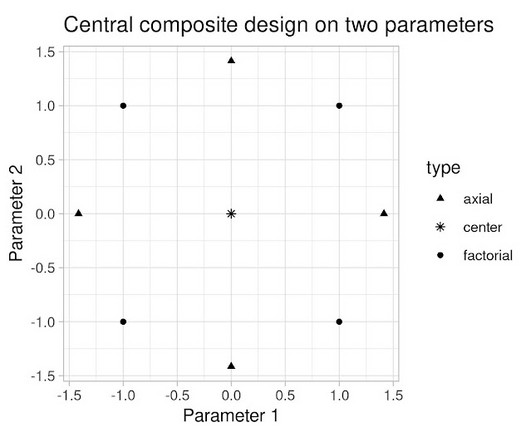
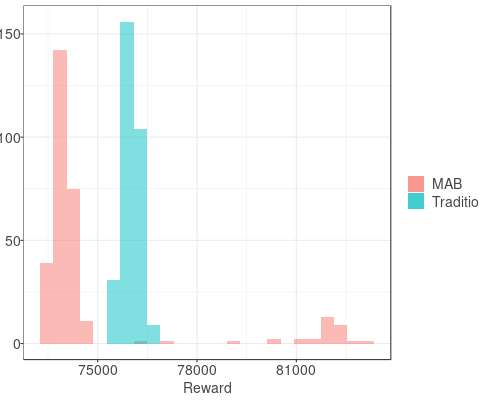
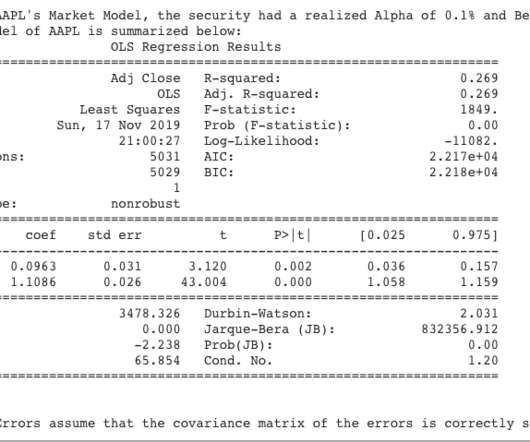
If $Y$ at that point is (statistically and practically) significantly better than our current operating point, and that point is deemed acceptable, we update the system parameters to this better value. Crucially, it takes into account the uncertainty inherent in our experiments. Why experiment with several parameters concurrently?









Let's personalize your content