Bridging the Gap: How ‘Data in Place’ and ‘Data in Use’ Define Complete Data Observability
DataKitchen
SEPTEMBER 21, 2023
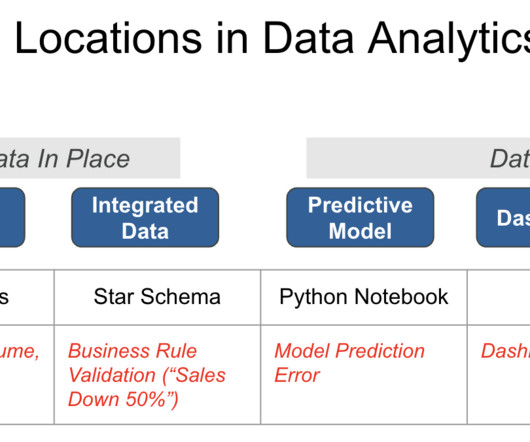
The uncertainty of not knowing where data issues will crop up next and the tiresome game of ‘who’s to blame’ when pinpointing the failure. In the context of Data in Place, validating data quality automatically with Business Domain Tests is imperative for ensuring the trustworthiness of your data assets.













Let's personalize your content