Towards optimal experimentation in online systems
The Unofficial Google Data Science Blog
APRIL 23, 2024
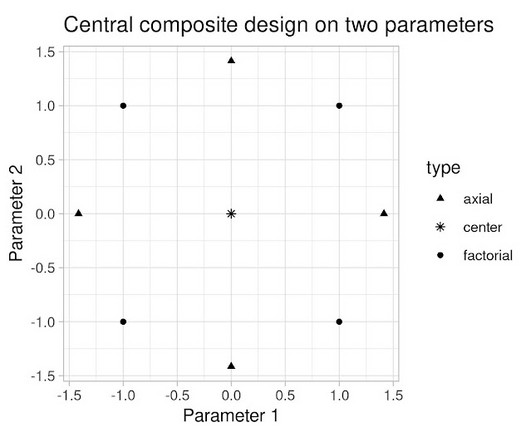
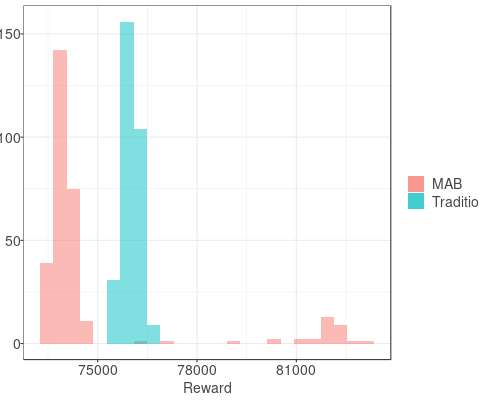
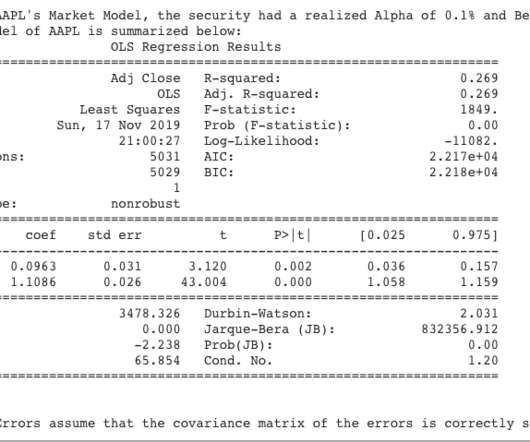
Crucially, it takes into account the uncertainty inherent in our experiments. To find optimal values of two parameters experimentally, the obvious strategy would be to experiment with and update them in separate, sequential stages. In this section we’ll discuss how we approach these two kinds of uncertainty with QCQP.











Let's personalize your content