Understanding the Differences Between Data Lakes and Data Warehouses
Smart Data Collective
AUGUST 28, 2021
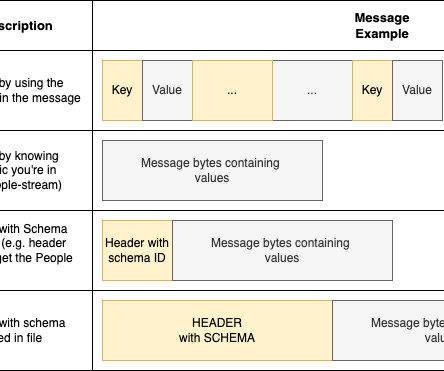
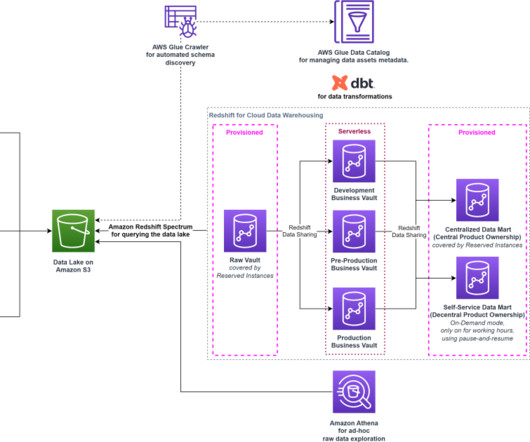
Data lakes and data warehouses are probably the two most widely used structures for storing data. Data Warehouses and Data Lakes in a Nutshell. A data warehouse is used as a central storage space for large amounts of structured data coming from various sources.





















Let's personalize your content