Real-time Data, Machine Learning, and Results: The Evidence Mounts
CIO Business Intelligence
OCTOBER 4, 2022
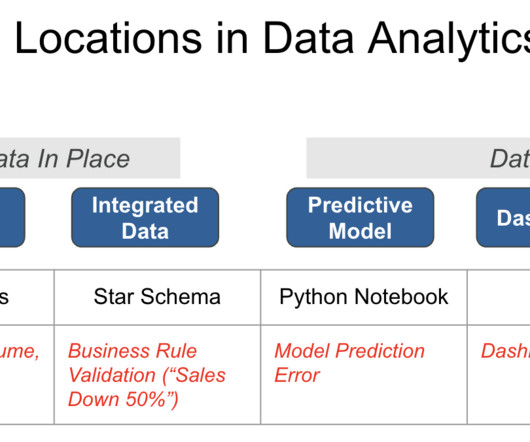
By Bryan Kirschner, Vice President, Strategy at DataStax. They identified two architectural elements for processing and delivering data: the “data platform,” which covers the sourcing, ingestion, and storage of data sets, and the “machine learning (ML) system,” which trains and productizes predictive models using input data.













Let's personalize your content