Explaining black-box models using attribute importance, PDPs, and LIME
Domino Data Lab
AUGUST 1, 2021
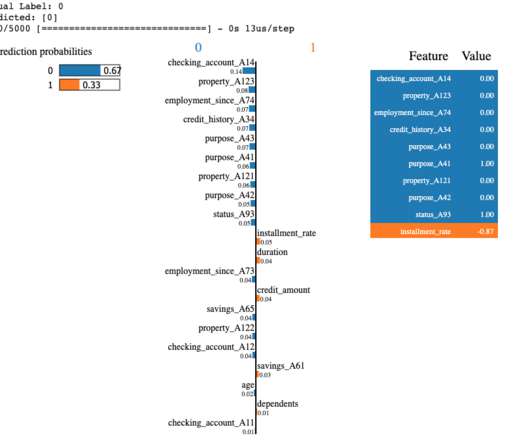
The need for interaction – complex decision making systems often rely on Human–Autonomy Teaming (HAT), where the outcome is produced by joint efforts of one or more humans and one or more autonomous agents. but it generally relies on measuring the entropy in the change of predictions given a perturbation of a feature.
















Let's personalize your content