Bringing an AI Product to Market
O'Reilly on Data
JULY 28, 2020
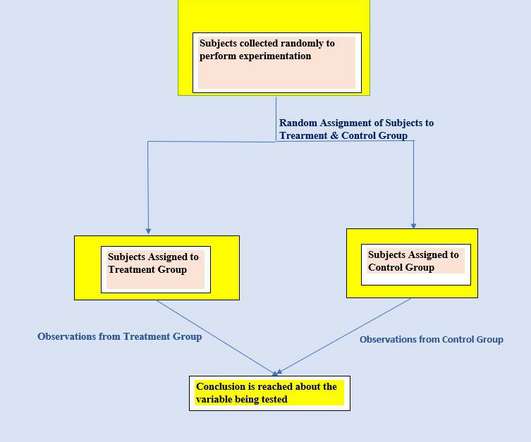
Product Managers are responsible for the successful development, testing, release, and adoption of a product, and for leading the team that implements those milestones. Without clarity in metrics, it’s impossible to do meaningful experimentation. Ongoing monitoring of critical metrics is yet another form of experimentation.




























Let's personalize your content